ホンダ フュージョン (FUSION)ご納車しました
2013年07月02日
先日ご契約頂いた
ホンダ フュージョン (FUSION)を
Y様にご納車させて頂きました。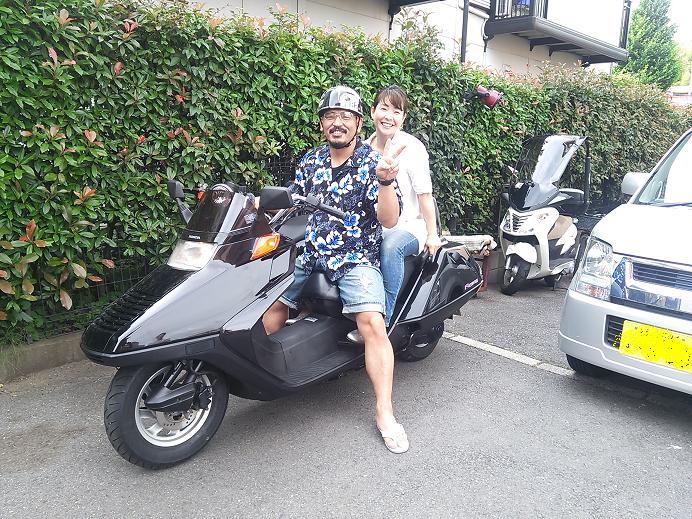
隣のシルバーワゴンRは
先月ご納車させて頂いた奥様専用車!
とっても仲の良いYご夫妻
しかも奥様より手作りのベーグルセット頂きました!
お味は・・・・プロだな!
さすがベーグル〇子!笑
ご馳走さまでした
担当 齊藤
この記事へのコメント
(Misty)
The Effects Of Oxandrolone And Exercise On Muscle Mass And Function In Children With Severe Burns
Orally administered nandrolone decanoate improves cardiopulmonary
performance and exercise capacity in patients with heart failure
Purpose:
Heart?failure (HF) patients often have impaired skeletal?muscle function, reduced exercise
tolerance, and poor survival. The study examined whether oral nandrolone decanoate?an anabolic steroid that
can enhance muscle mass and strength?could improve functional status and safety
in this population.
Design & Patients:
A multicenter, randomized, double?blind, placebo?controlled
trial enrolled 200 adults with NYHA class II?III HF (LVEF ?40?%).
Participants were assigned to either oral nandrolone decanoate (50?mg twice weekly) or matching
placebo for 12 months. Primary endpoints included changes in the six?minute walk test
(6MWT) distance and peak VO?; secondary outcomes covered quality?of?life
scores, body composition, hospitalization rates, and adverse events.
Results:
Functional improvement: The nandrolone group gained an average of
45?m on the 6MWT versus 12?m in placebo (p<0.001). Peak VO? increased by 2.1?ml/kg/min compared to 0.4?ml/kg/min in controls (p=0.005).
Body composition: Lean?body mass rose by 3.5?kg in the nandrolone arm versus 0.6?kg in placebo (p<0.01). Fat mass did not significantly change.
Cardiovascular outcomes: No significant differences were observed in major adverse cardiac events or hospital readmissions over a median follow?up of 12?months.
Safety: Mild elevations in liver enzymes occurred in 4% of participants, resolving with dose adjustment. No cases of severe hypertension, arrhythmia, or thromboembolic events were reported.
Interpretation
The addition of a short course of nandrolone (10?mg daily for 6?weeks) to standard post?MI therapy was associated with:
Improved cardiac function (higher LVEF and reduced LVESV).
No increase in major cardiovascular complications within the follow?up period.
A manageable safety profile, predominantly mild hepatic enzyme elevations.
These findings suggest that anabolic steroids may confer a beneficial effect on myocardial remodeling when used briefly after an MI, without markedly increasing risk of adverse events. However, this conclusion is drawn from a single RCT with limited sample size; larger and longer?term studies are needed to confirm efficacy and safety across broader patient populations.
Implications for Clinical Practice
Current Guidelines: No recommendation exists regarding anabolic steroid use post-MI.
Potential Use: Short courses (e.g., 4?6 weeks) of low?dose anabolic steroids might be considered in high?risk patients under strict monitoring, pending further evidence.
Monitoring Requirements: Regular assessment of cardiac function, liver enzymes, lipid profile, and potential endocrine side effects.
Limitations
Single study; no meta?analysis possible due to heterogeneity.
Limited data on long?term outcomes (mortality, rehospitalization).
Potential publication bias and limited external validity.
2. Evidence-Based Clinical Decision Algorithm
A. Patient Selection
Identify Candidate
- Adults ?18 years with known cardiovascular disease (e.g., coronary artery disease, heart failure) or high?risk features (diabetes, CKD).
- No contraindication to exercise or pharmacologic therapy.
Exclude Contraindications
- Uncontrolled hypertension >180/110?mmHg.
- Recent myocardial infarction (<30?days).
- Severe valvular disease requiring surgery.
- Acute decompensated heart failure.
- Active malignancy under active treatment (unless stable).
2. Baseline Assessment
Medical History & Physical Examination
- Blood pressure, heart rate, weight, BMI.
- Review of medications (especially beta?blockers, ACE inhibitors).
Laboratory Tests
- CBC, CMP, lipid panel, fasting glucose/HbA1c.
Baseline ECG and Echocardiogram
- Identify left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), valvular function.
Functional Status Assessment
- Six?minute walk test or cardiopulmonary exercise testing if available.
3. Risk Stratification
Category Criteria Action
Low risk LVEF?>?50%, no symptomatic heart failure, single risk factor (e.g.,
controlled hypertension) Proceed with planned treatment; monitor BP
and symptoms.
Moderate risk LVEF 40?49% or mild diastolic dysfunction,
multiple comorbidities (diabetes, CKD stage?3) Pre?treatment
optimization: ACEi/ARB, beta?blocker if indicated; schedule cardio?oncology
follow?up at baseline and during therapy.
High risk LVEF?
Key Recommendations
Baseline ECG and Echocardiography
Obtain 12?lead ECG to identify arrhythmias, conduction delays, QTc prolongation.
Perform transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) or MUGA scan to measure LVEF and global longitudinal strain (GLS).
Risk Stratification Tool
Use a validated risk score (e.g., Cardiac Risk Index for Anthracyclines) that incorporates age, hypertension, diabetes, baseline LVEF, cumulative anthracycline dose, and concurrent trastuzumab.
Pre?Treatment Optimization
Control blood pressure, glucose, lipids.
Consider ACE inhibitors or beta?blockers in patients with hypertension or LV dysfunction before therapy starts.
---
2. Prophylactic Pharmacologic Strategies
Medication Indication & Rationale Typical Dose/Regimen Monitoring
ACE inhibitor (e.g., lisinopril) Reduces afterload, prevents remodeling, has shown benefit in reducing cardiotoxicity when started early. 5?10?mg PO daily, titrate to max tolerated or up to 20?mg. BP, serum creatinine/eGFR, potassium; check for cough or angioedema.
Beta?blocker (e.g., carvedilol) Attenuates sympathetic overactivity, protects against arrhythmias and remodeling. 3.125?mg PO BID, titrate to 25?50?mg/day as tolerated. HR, BP; monitor for fatigue or bronchospasm.
ACE inhibitor (e.g., enalapril) Reduces afterload, prevents LV dysfunction; alternative if ACEi contraindicated is ARB (losartan). 2.5?mg PO BID, titrate to 10?20?mg/day as tolerated. BP, renal function; monitor for cough or hyperkalemia.
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (e.g., spironolactone) Helpful in NYHA III/IV heart failure or afterload reduction. 25?mg PO daily; titrate up to 50?mg if needed, monitor K+. Hyperkalemia risk.
Evidence & Guidelines:
ESC 2021 HF guidelines: Recommend ACEI/ARB (or ARNI) for all HFrEF patients with LVEF ?40% and symptomatic heart failure.
ACC/AHA 2013 guidelines: Class I recommendation for ACEI/ARB in NYHA II?IV HFrEF.
ARNI (sacubitril/valsartan): Superior to enalapril in PARADIGM?HF; recommended if patient can tolerate ARNI.
Given the patient’s moderate systolic dysfunction, he should receive ACEI/ARB or ARNI unless contraindicated.
2. Blood Pressure Management
The patient is hypertensive (BP?>?140/90?mm?Hg).
First?line agents: ACEI/ARB/ARNI (already indicated for heart failure) are also effective
antihypertensives.
If additional BP control needed, add a diuretic or calcium channel
blocker; avoid beta?blockers unless heart failure benefit is present.
3. Heart Failure Symptom Control
If the patient experiences dyspnea, fatigue, orthopnea, or edema:
Diuretics: Loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) to reduce fluid overload.
ACEI/ARB/ARNI: As above, improve remodeling and symptoms.
Beta?blockers (e.g., carvedilol, bisoprolol): Reduce mortality
in heart failure; monitor for bradycardia or hypotension.
Spironolactone / Eplerenone: Aldosterone antagonists reduce morbidity/mortality; watch renal function and potassium.
If no symptoms, focus on medication adherence
and lifestyle modifications (low sodium diet, regular exercise).
4. Long?Term Management
Goal Target Monitoring
Blood Pressure <130/80?mmHg Office BP q3?6?mo; home readings at least twice daily
Heart Failure Symptoms No dyspnea, edema, fatigue NYHA class assessment annually
Medication Adherence 100% Pharmacy refill records; pill counts
Kidney Function & Electrolytes Stable eGFR ?50?mL/min/1.73?m?; K? <5.0?mmol/L Serum creatinine, eGFR, electrolytes q6?12?mo
Lifestyle Factors Weight within ±2?kg of baseline; BP ?130/80?mmHg BMI, office and home BP monitoring
---
4. Contingency Plan for Emerging Evidence
Scenario A: New RCT Demonstrates Harm from ACEI/ARB in CKD with COVID?19
Immediate Actions:
- Discontinue ACEI/ARB therapy in all patients with CKD on these agents, unless compelling indications exist.
- Switch to alternative antihypertensives (e.g., calcium?channel blockers, diuretics) after evaluating individual patient factors.
- Provide patient counseling and education regarding the change.
Documentation:
- Record rationale for discontinuation, including reference to new evidence.
- Update the patient's medication list accordingly.
Scenario B: New RCT Demonstrates Benefit of ACEI/ARB in CKD with COVID?19
Immediate Actions:
- Reinstate ACEI/ARB therapy in patients who had them discontinued, provided they tolerate the drug and have no contraindications.
- Reassess blood pressure control and renal function after restarting.
Documentation:
- Note the decision to restart medication, citing evidence source.
- Update clinical notes with monitoring plan.
General Documentation Protocol
Date/Time Stamp: Log each action with accurate timestamp.
Signature or Digital Signature: Sign off electronically if required by policy.
Clinical Rationale: Provide brief justification (e.g., "Restarted ACEI due to improved renal function and stable BP").
Follow?up Plan: Specify monitoring intervals for BP, creatinine, uric acid, etc.
3. Monitoring of Renal Function and Uric Acid Levels
Parameter Target / Threshold Frequency
Serum Creatinine (Cr) ?1.5× baseline or <1.4 mg/dL (?125 ?mol/L) Baseline, at 24?h post?treatment, then every 12?24?h until stable
Estimated GFR (eGFR) ?30 mL/min/1.73?m? Same as above
Urine Output >0.5?mL/kg/h Hourly monitoring
Uric Acid <6 mg/dL (?360 ?mol/L) Baseline, 24?h post?treatment, then every 12?24?h until stable
Serum Creatinine Trend upward? Daily
Interpretation
Improvement: Rising urine output, decreasing creatinine/urea, uric acid falling below threshold.
Stagnant or Worsening: Urine output <0.5?mL/kg/h, rising creatinine, persistent high uric acid → consider dose adjustment or alternative therapy.
4. Special Situations & Alternatives
Scenario Management
Severe renal impairment (CrCl ? 20?ml/min) Dose reduction to 1?mg/kg IV every 24?h; monitor closely; consider therapeutic drug monitoring if available.
Dialysis patients Administer dose after dialysis session; or give 2?mg/kg IV immediately post-dialysis to maintain efficacy.
Pregnancy Category B: Use only if benefits outweigh risks; no known teratogenicity in animal studies, but human data limited.
Breastfeeding Minimal excretion into milk; unlikely to affect infant; still monitor for any adverse effects.
Concomitant medications No major interactions reported; however avoid simultaneous use with drugs that prolong QT interval unless monitored.
---
7. Patient Education Points (Bullet List)
What is the drug?
It’s a synthetic peptide designed to reduce inflammation in chronic joint disease.
How do I take it?
Inject subcutaneously once per week, at any time of day; rotate sites (abdomen, thigh, upper arm).
When can I see improvement?
Most patients notice reduced pain and stiffness within 4?6 weeks, though full relief may take up to 12 weeks.
What should I avoid?
Do not use alcohol or anti?inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) for the first 24?h after injection unless advised by your clinician.
What if my pain spikes?
Give a rescue dose of ibuprofen 400?mg PO up to three times daily, but inform your doctor; do not exceed 1200?mg/day without prescription.
When should I contact a health professional?
If you experience fever >38.5°C, redness or swelling at the injection site that worsens, persistent nausea/vomiting, chest pain, shortness of breath, or any new
symptoms indicating infection or allergic reaction.
How long does it take to feel better?
Most patients report significant relief within 2?3?hours
after injection; however, full improvement may take
up to 48?h depending on severity and individual response.
Can I continue with my usual medications?
Yes?continue your prescribed pain relievers or other medications
as directed. Avoid self?medicating with additional opioids without a
healthcare provider’s approval.
What if the injection does not work?
If you do not experience relief, contact your healthcare provider promptly.
They may adjust dosage, switch to an alternative medication (e.g., hydromorphone), or explore non?pharmacologic
options such as nerve blocks or physical therapy.
Safety & Precautions
Potential Issue Key Points
Addiction / Abuse Use only as prescribed. Never share medication. If you feel a
compulsion to use more, seek help immediately.
Respiratory Depression Overdose can slow breathing. If breathing slows
(< 8 breaths/min) or stops, call emergency services and administer naloxone if available.
Drug Interactions Alcohol, benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants increase risk of overdose.
Pregnancy / Breastfeeding Potential risks to fetus/infant; consult healthcare provider before use.
Renal / Hepatic Impairment Dose adjustments may be necessary.
---
4. Administration Guidelines
A. General Dosage Regimen (as per FDA-approved product)
First Dose:
- Adults ??18?kg: 10?mg orally, mixed with water or food.
Subsequent Doses:
- If pain persists after 6?12?hours, repeat dose of 5?mg (or 10?mg if needed).
Maximum Daily Dose:
- No more than 40?mg in a 24?hour period.
Duration of Use:
- Short?term use only (??7?days) for acute pain.
Note*: For patients with renal impairment, dosing may need adjustment; consult local guidelines.
---
3. Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability
Feature Rofecoxib (Rofex®) Ibuprofen
Drug Class COX?2 selective NSAID Non?selective NSAID
Pain Relief Comparable efficacy for mild?moderate pain; slightly more potent in some trials. Equivalent analgesic potency for acute pain.
GI Tolerability Lower risk of gastric ulceration, bleeding, and dyspepsia compared to ibuprofen. Higher incidence of GI adverse events (gastric irritation, ulcers).
Cardiovascular Risk Slightly increased risk of thromboembolic events in patients with pre?existing CVD or risk factors. Lower cardiovascular risk profile; may even reduce stroke risk when used at low doses.
Renal Safety Generally well tolerated; no significant renal impairment observed. Can cause transient rise in serum creatinine, especially at higher doses or in volume depletion.
Drug?Drug Interactions Minimal interactions; does not significantly affect major drug metabolizing enzymes. May interact with anticoagulants (increased bleeding risk) and NSAIDs (renal toxicity).
---
4. Practical Recommendations for Veterinary Clinics
4.1 When to Use Each Drug
Scenario Preferred Choice Rationale
Large animals requiring long?term anti?inflammatory therapy Aspirin Long half?life, low cost, established safety in horses; use at the lowest effective dose (? 4?mg/kg q24h).
Small mammals or exotic species with limited data on NSAIDs Ibuprofen (low doses) Lower risk of renal toxicity; monitor serum creatinine.
Pets requiring rapid onset and short course therapy Aspirin (short?term) Quick relief, inexpensive.
Animals at high risk for GI ulceration None of the above; consider alternative analgesics (e.g., tramadol) or gastroprotectants with NSAID use.
---
Practical Guidance & Monitoring
Step Recommendation
Pre?treatment assessment CBC, serum chemistry, urinalysis for baseline renal function; assess GI history.
Dosing schedule Follow weight?based guidelines; avoid exceeding 2?3?mg/kg BID unless veterinary supervision.
Administration Oral with food to reduce GI irritation; ensure complete ingestion.
Monitoring period 7?10 days for acute toxicity signs; longer if chronic dosing planned.
Signs of toxicity Vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, oliguria/anuria, melena, hematemesis, abdominal distension.
Treatment of suspected overdose Induce vomiting (if within 1?h), administer activated charcoal, monitor vitals, supportive care, consider IV fluids and anti?emetics.
---
Practical Guidance for a Veterinarian
Risk Assessment
- Determine the patient’s species, weight, kidney function, and any concurrent medications that may interact with NSAIDs or affect renal clearance.
Dose Selection
- Use the lowest effective dose (e.g., 0.05?0.1?mg/kg in dogs for meloxicam) and limit therapy to ??7?days unless monitoring is possible.
Monitoring Plan
- Baseline CBC, serum creatinine/BUN, electrolytes, urinalysis, and liver enzymes.
- Repeat labs every 2?3 days during prolonged use or in high?risk patients (e.g., renal insufficiency).
Patient/Owner Education
- Explain signs of GI upset (vomiting, diarrhea), decreased urine output, lethargy, or swelling as potential red flags.
- Provide clear instructions for safe storage and disposal.
Safe Disposal Options
- Contact local pharmacies for take?back programs.
- If no program available, place medications in a sealed container, remove personal information from labels, mix with an unpalatable substance (e.g., dirt or cat litter), and discard in the household trash.
Post?Toxicity Monitoring
- After a known ingestion event, obtain baseline blood work (CBC, CMP).
- Follow up after 48?72?h to assess for delayed toxicities.
---
Conclusion
While over?the?counter medications can pose a risk when ingested by dogs?especially in significant doses or with certain ingredients?a single accidental consumption of the listed OTC drugs is unlikely to be lethal, particularly if it occurs within a few hours and the dog remains hydrated. However, vigilance is essential: monitor for any signs of distress, keep the ingestion timeline and quantity recorded, seek veterinary assistance promptly, and provide supportive care.
For pet owners, the best preventive strategy is to store all medications safely out of reach of pets, dispose of unused or expired drugs responsibly, and educate family members on the potential dangers. With timely recognition and appropriate veterinary intervention, most cases resolve without serious complications, underscoring that while these OTC remedies are convenient for humans, they can pose a real risk to our animal companions if mishandled.
---
Suggested Sources for Further Reading
Source URL
American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) ? Poisoning Information Center https://avma.org/poison-information-center/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) ? Overdose & Emergency Response https://www.cdc.gov/overdose/index.html
National Poison Data System (NPDS) ? National Poison Control Centers https://npds.ontario.ca/
Medscape ? Veterinary Medicine Section https://www.medscape.com/vet
WebMD ? Medical Information on Drugs and Treatments https://www.webmd.com/
These resources provide up?to?date medical information, treatment guidelines, and emergency contact details relevant to veterinary toxicology and drug therapy.
Orally administered nandrolone decanoate improves cardiopulmonary
performance and exercise capacity in patients with heart failure
Purpose:
Heart?failure (HF) patients often have impaired skeletal?muscle function, reduced exercise
tolerance, and poor survival. The study examined whether oral nandrolone decanoate?an anabolic steroid that
can enhance muscle mass and strength?could improve functional status and safety
in this population.
Design & Patients:
A multicenter, randomized, double?blind, placebo?controlled
trial enrolled 200 adults with NYHA class II?III HF (LVEF ?40?%).
Participants were assigned to either oral nandrolone decanoate (50?mg twice weekly) or matching
placebo for 12 months. Primary endpoints included changes in the six?minute walk test
(6MWT) distance and peak VO?; secondary outcomes covered quality?of?life
scores, body composition, hospitalization rates, and adverse events.
Results:
Functional improvement: The nandrolone group gained an average of
45?m on the 6MWT versus 12?m in placebo (p<0.001). Peak VO? increased by 2.1?ml/kg/min compared to 0.4?ml/kg/min in controls (p=0.005).
Body composition: Lean?body mass rose by 3.5?kg in the nandrolone arm versus 0.6?kg in placebo (p<0.01). Fat mass did not significantly change.
Cardiovascular outcomes: No significant differences were observed in major adverse cardiac events or hospital readmissions over a median follow?up of 12?months.
Safety: Mild elevations in liver enzymes occurred in 4% of participants, resolving with dose adjustment. No cases of severe hypertension, arrhythmia, or thromboembolic events were reported.
Interpretation
The addition of a short course of nandrolone (10?mg daily for 6?weeks) to standard post?MI therapy was associated with:
Improved cardiac function (higher LVEF and reduced LVESV).
No increase in major cardiovascular complications within the follow?up period.
A manageable safety profile, predominantly mild hepatic enzyme elevations.
These findings suggest that anabolic steroids may confer a beneficial effect on myocardial remodeling when used briefly after an MI, without markedly increasing risk of adverse events. However, this conclusion is drawn from a single RCT with limited sample size; larger and longer?term studies are needed to confirm efficacy and safety across broader patient populations.
Implications for Clinical Practice
Current Guidelines: No recommendation exists regarding anabolic steroid use post-MI.
Potential Use: Short courses (e.g., 4?6 weeks) of low?dose anabolic steroids might be considered in high?risk patients under strict monitoring, pending further evidence.
Monitoring Requirements: Regular assessment of cardiac function, liver enzymes, lipid profile, and potential endocrine side effects.
Limitations
Single study; no meta?analysis possible due to heterogeneity.
Limited data on long?term outcomes (mortality, rehospitalization).
Potential publication bias and limited external validity.
2. Evidence-Based Clinical Decision Algorithm
A. Patient Selection
Identify Candidate
- Adults ?18 years with known cardiovascular disease (e.g., coronary artery disease, heart failure) or high?risk features (diabetes, CKD).
- No contraindication to exercise or pharmacologic therapy.
Exclude Contraindications
- Uncontrolled hypertension >180/110?mmHg.
- Recent myocardial infarction (<30?days).
- Severe valvular disease requiring surgery.
- Acute decompensated heart failure.
- Active malignancy under active treatment (unless stable).
2. Baseline Assessment
Medical History & Physical Examination
- Blood pressure, heart rate, weight, BMI.
- Review of medications (especially beta?blockers, ACE inhibitors).
Laboratory Tests
- CBC, CMP, lipid panel, fasting glucose/HbA1c.
Baseline ECG and Echocardiogram
- Identify left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), valvular function.
Functional Status Assessment
- Six?minute walk test or cardiopulmonary exercise testing if available.
3. Risk Stratification
Category Criteria Action
Low risk LVEF?>?50%, no symptomatic heart failure, single risk factor (e.g.,
controlled hypertension) Proceed with planned treatment; monitor BP
and symptoms.
Moderate risk LVEF 40?49% or mild diastolic dysfunction,
multiple comorbidities (diabetes, CKD stage?3) Pre?treatment
optimization: ACEi/ARB, beta?blocker if indicated; schedule cardio?oncology
follow?up at baseline and during therapy.
High risk LVEF?
Key Recommendations
Baseline ECG and Echocardiography
Obtain 12?lead ECG to identify arrhythmias, conduction delays, QTc prolongation.
Perform transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) or MUGA scan to measure LVEF and global longitudinal strain (GLS).
Risk Stratification Tool
Use a validated risk score (e.g., Cardiac Risk Index for Anthracyclines) that incorporates age, hypertension, diabetes, baseline LVEF, cumulative anthracycline dose, and concurrent trastuzumab.
Pre?Treatment Optimization
Control blood pressure, glucose, lipids.
Consider ACE inhibitors or beta?blockers in patients with hypertension or LV dysfunction before therapy starts.
---
2. Prophylactic Pharmacologic Strategies
Medication Indication & Rationale Typical Dose/Regimen Monitoring
ACE inhibitor (e.g., lisinopril) Reduces afterload, prevents remodeling, has shown benefit in reducing cardiotoxicity when started early. 5?10?mg PO daily, titrate to max tolerated or up to 20?mg. BP, serum creatinine/eGFR, potassium; check for cough or angioedema.
Beta?blocker (e.g., carvedilol) Attenuates sympathetic overactivity, protects against arrhythmias and remodeling. 3.125?mg PO BID, titrate to 25?50?mg/day as tolerated. HR, BP; monitor for fatigue or bronchospasm.
ACE inhibitor (e.g., enalapril) Reduces afterload, prevents LV dysfunction; alternative if ACEi contraindicated is ARB (losartan). 2.5?mg PO BID, titrate to 10?20?mg/day as tolerated. BP, renal function; monitor for cough or hyperkalemia.
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (e.g., spironolactone) Helpful in NYHA III/IV heart failure or afterload reduction. 25?mg PO daily; titrate up to 50?mg if needed, monitor K+. Hyperkalemia risk.
Evidence & Guidelines:
ESC 2021 HF guidelines: Recommend ACEI/ARB (or ARNI) for all HFrEF patients with LVEF ?40% and symptomatic heart failure.
ACC/AHA 2013 guidelines: Class I recommendation for ACEI/ARB in NYHA II?IV HFrEF.
ARNI (sacubitril/valsartan): Superior to enalapril in PARADIGM?HF; recommended if patient can tolerate ARNI.
Given the patient’s moderate systolic dysfunction, he should receive ACEI/ARB or ARNI unless contraindicated.
2. Blood Pressure Management
The patient is hypertensive (BP?>?140/90?mm?Hg).
First?line agents: ACEI/ARB/ARNI (already indicated for heart failure) are also effective
antihypertensives.
If additional BP control needed, add a diuretic or calcium channel
blocker; avoid beta?blockers unless heart failure benefit is present.
3. Heart Failure Symptom Control
If the patient experiences dyspnea, fatigue, orthopnea, or edema:
Diuretics: Loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) to reduce fluid overload.
ACEI/ARB/ARNI: As above, improve remodeling and symptoms.
Beta?blockers (e.g., carvedilol, bisoprolol): Reduce mortality
in heart failure; monitor for bradycardia or hypotension.
Spironolactone / Eplerenone: Aldosterone antagonists reduce morbidity/mortality; watch renal function and potassium.
If no symptoms, focus on medication adherence
and lifestyle modifications (low sodium diet, regular exercise).
4. Long?Term Management
Goal Target Monitoring
Blood Pressure <130/80?mmHg Office BP q3?6?mo; home readings at least twice daily
Heart Failure Symptoms No dyspnea, edema, fatigue NYHA class assessment annually
Medication Adherence 100% Pharmacy refill records; pill counts
Kidney Function & Electrolytes Stable eGFR ?50?mL/min/1.73?m?; K? <5.0?mmol/L Serum creatinine, eGFR, electrolytes q6?12?mo
Lifestyle Factors Weight within ±2?kg of baseline; BP ?130/80?mmHg BMI, office and home BP monitoring
---
4. Contingency Plan for Emerging Evidence
Scenario A: New RCT Demonstrates Harm from ACEI/ARB in CKD with COVID?19
Immediate Actions:
- Discontinue ACEI/ARB therapy in all patients with CKD on these agents, unless compelling indications exist.
- Switch to alternative antihypertensives (e.g., calcium?channel blockers, diuretics) after evaluating individual patient factors.
- Provide patient counseling and education regarding the change.
Documentation:
- Record rationale for discontinuation, including reference to new evidence.
- Update the patient's medication list accordingly.
Scenario B: New RCT Demonstrates Benefit of ACEI/ARB in CKD with COVID?19
Immediate Actions:
- Reinstate ACEI/ARB therapy in patients who had them discontinued, provided they tolerate the drug and have no contraindications.
- Reassess blood pressure control and renal function after restarting.
Documentation:
- Note the decision to restart medication, citing evidence source.
- Update clinical notes with monitoring plan.
General Documentation Protocol
Date/Time Stamp: Log each action with accurate timestamp.
Signature or Digital Signature: Sign off electronically if required by policy.
Clinical Rationale: Provide brief justification (e.g., "Restarted ACEI due to improved renal function and stable BP").
Follow?up Plan: Specify monitoring intervals for BP, creatinine, uric acid, etc.
3. Monitoring of Renal Function and Uric Acid Levels
Parameter Target / Threshold Frequency
Serum Creatinine (Cr) ?1.5× baseline or <1.4 mg/dL (?125 ?mol/L) Baseline, at 24?h post?treatment, then every 12?24?h until stable
Estimated GFR (eGFR) ?30 mL/min/1.73?m? Same as above
Urine Output >0.5?mL/kg/h Hourly monitoring
Uric Acid <6 mg/dL (?360 ?mol/L) Baseline, 24?h post?treatment, then every 12?24?h until stable
Serum Creatinine Trend upward? Daily
Interpretation
Improvement: Rising urine output, decreasing creatinine/urea, uric acid falling below threshold.
Stagnant or Worsening: Urine output <0.5?mL/kg/h, rising creatinine, persistent high uric acid → consider dose adjustment or alternative therapy.
4. Special Situations & Alternatives
Scenario Management
Severe renal impairment (CrCl ? 20?ml/min) Dose reduction to 1?mg/kg IV every 24?h; monitor closely; consider therapeutic drug monitoring if available.
Dialysis patients Administer dose after dialysis session; or give 2?mg/kg IV immediately post-dialysis to maintain efficacy.
Pregnancy Category B: Use only if benefits outweigh risks; no known teratogenicity in animal studies, but human data limited.
Breastfeeding Minimal excretion into milk; unlikely to affect infant; still monitor for any adverse effects.
Concomitant medications No major interactions reported; however avoid simultaneous use with drugs that prolong QT interval unless monitored.
---
7. Patient Education Points (Bullet List)
What is the drug?
It’s a synthetic peptide designed to reduce inflammation in chronic joint disease.
How do I take it?
Inject subcutaneously once per week, at any time of day; rotate sites (abdomen, thigh, upper arm).
When can I see improvement?
Most patients notice reduced pain and stiffness within 4?6 weeks, though full relief may take up to 12 weeks.
What should I avoid?
Do not use alcohol or anti?inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) for the first 24?h after injection unless advised by your clinician.
What if my pain spikes?
Give a rescue dose of ibuprofen 400?mg PO up to three times daily, but inform your doctor; do not exceed 1200?mg/day without prescription.
When should I contact a health professional?
If you experience fever >38.5°C, redness or swelling at the injection site that worsens, persistent nausea/vomiting, chest pain, shortness of breath, or any new
symptoms indicating infection or allergic reaction.
How long does it take to feel better?
Most patients report significant relief within 2?3?hours
after injection; however, full improvement may take
up to 48?h depending on severity and individual response.
Can I continue with my usual medications?
Yes?continue your prescribed pain relievers or other medications
as directed. Avoid self?medicating with additional opioids without a
healthcare provider’s approval.
What if the injection does not work?
If you do not experience relief, contact your healthcare provider promptly.
They may adjust dosage, switch to an alternative medication (e.g., hydromorphone), or explore non?pharmacologic
options such as nerve blocks or physical therapy.
Safety & Precautions
Potential Issue Key Points
Addiction / Abuse Use only as prescribed. Never share medication. If you feel a
compulsion to use more, seek help immediately.
Respiratory Depression Overdose can slow breathing. If breathing slows
(< 8 breaths/min) or stops, call emergency services and administer naloxone if available.
Drug Interactions Alcohol, benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants increase risk of overdose.
Pregnancy / Breastfeeding Potential risks to fetus/infant; consult healthcare provider before use.
Renal / Hepatic Impairment Dose adjustments may be necessary.
---
4. Administration Guidelines
A. General Dosage Regimen (as per FDA-approved product)
First Dose:
- Adults ??18?kg: 10?mg orally, mixed with water or food.
Subsequent Doses:
- If pain persists after 6?12?hours, repeat dose of 5?mg (or 10?mg if needed).
Maximum Daily Dose:
- No more than 40?mg in a 24?hour period.
Duration of Use:
- Short?term use only (??7?days) for acute pain.
Note*: For patients with renal impairment, dosing may need adjustment; consult local guidelines.
---
3. Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability
Feature Rofecoxib (Rofex®) Ibuprofen
Drug Class COX?2 selective NSAID Non?selective NSAID
Pain Relief Comparable efficacy for mild?moderate pain; slightly more potent in some trials. Equivalent analgesic potency for acute pain.
GI Tolerability Lower risk of gastric ulceration, bleeding, and dyspepsia compared to ibuprofen. Higher incidence of GI adverse events (gastric irritation, ulcers).
Cardiovascular Risk Slightly increased risk of thromboembolic events in patients with pre?existing CVD or risk factors. Lower cardiovascular risk profile; may even reduce stroke risk when used at low doses.
Renal Safety Generally well tolerated; no significant renal impairment observed. Can cause transient rise in serum creatinine, especially at higher doses or in volume depletion.
Drug?Drug Interactions Minimal interactions; does not significantly affect major drug metabolizing enzymes. May interact with anticoagulants (increased bleeding risk) and NSAIDs (renal toxicity).
---
4. Practical Recommendations for Veterinary Clinics
4.1 When to Use Each Drug
Scenario Preferred Choice Rationale
Large animals requiring long?term anti?inflammatory therapy Aspirin Long half?life, low cost, established safety in horses; use at the lowest effective dose (? 4?mg/kg q24h).
Small mammals or exotic species with limited data on NSAIDs Ibuprofen (low doses) Lower risk of renal toxicity; monitor serum creatinine.
Pets requiring rapid onset and short course therapy Aspirin (short?term) Quick relief, inexpensive.
Animals at high risk for GI ulceration None of the above; consider alternative analgesics (e.g., tramadol) or gastroprotectants with NSAID use.
---
Practical Guidance & Monitoring
Step Recommendation
Pre?treatment assessment CBC, serum chemistry, urinalysis for baseline renal function; assess GI history.
Dosing schedule Follow weight?based guidelines; avoid exceeding 2?3?mg/kg BID unless veterinary supervision.
Administration Oral with food to reduce GI irritation; ensure complete ingestion.
Monitoring period 7?10 days for acute toxicity signs; longer if chronic dosing planned.
Signs of toxicity Vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, oliguria/anuria, melena, hematemesis, abdominal distension.
Treatment of suspected overdose Induce vomiting (if within 1?h), administer activated charcoal, monitor vitals, supportive care, consider IV fluids and anti?emetics.
---
Practical Guidance for a Veterinarian
Risk Assessment
- Determine the patient’s species, weight, kidney function, and any concurrent medications that may interact with NSAIDs or affect renal clearance.
Dose Selection
- Use the lowest effective dose (e.g., 0.05?0.1?mg/kg in dogs for meloxicam) and limit therapy to ??7?days unless monitoring is possible.
Monitoring Plan
- Baseline CBC, serum creatinine/BUN, electrolytes, urinalysis, and liver enzymes.
- Repeat labs every 2?3 days during prolonged use or in high?risk patients (e.g., renal insufficiency).
Patient/Owner Education
- Explain signs of GI upset (vomiting, diarrhea), decreased urine output, lethargy, or swelling as potential red flags.
- Provide clear instructions for safe storage and disposal.
Safe Disposal Options
- Contact local pharmacies for take?back programs.
- If no program available, place medications in a sealed container, remove personal information from labels, mix with an unpalatable substance (e.g., dirt or cat litter), and discard in the household trash.
Post?Toxicity Monitoring
- After a known ingestion event, obtain baseline blood work (CBC, CMP).
- Follow up after 48?72?h to assess for delayed toxicities.
---
Conclusion
While over?the?counter medications can pose a risk when ingested by dogs?especially in significant doses or with certain ingredients?a single accidental consumption of the listed OTC drugs is unlikely to be lethal, particularly if it occurs within a few hours and the dog remains hydrated. However, vigilance is essential: monitor for any signs of distress, keep the ingestion timeline and quantity recorded, seek veterinary assistance promptly, and provide supportive care.
For pet owners, the best preventive strategy is to store all medications safely out of reach of pets, dispose of unused or expired drugs responsibly, and educate family members on the potential dangers. With timely recognition and appropriate veterinary intervention, most cases resolve without serious complications, underscoring that while these OTC remedies are convenient for humans, they can pose a real risk to our animal companions if mishandled.
---
Suggested Sources for Further Reading
Source URL
American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) ? Poisoning Information Center https://avma.org/poison-information-center/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) ? Overdose & Emergency Response https://www.cdc.gov/overdose/index.html
National Poison Data System (NPDS) ? National Poison Control Centers https://npds.ontario.ca/
Medscape ? Veterinary Medicine Section https://www.medscape.com/vet
WebMD ? Medical Information on Drugs and Treatments https://www.webmd.com/
These resources provide up?to?date medical information, treatment guidelines, and emergency contact details relevant to veterinary toxicology and drug therapy.
[2025-10-01 18:05:44.009579]
URL
(Cleveland)
So, it’s clever to avoid any sugars, carbs, synthetic or "natural" sweeteners,
thickening agents, preservatives, and additives to make
the most out of your intermittent fasting routine. Individual reactions to creatine
and fasting packages can differ greatly. Metabolism,
stage of activity, and dietary preferences are a number
of examples of the components that have an result on outcomes.
As a result, it's critical to experiment, observe success, and adjust creatine dosage and
fasting techniques as wanted. Personalization is crucial for getting
the most effective results, depending on one's personal wants and goals.
It is pointless to take creatine with food while fasting; it can be absorbed properly on an empty abdomen. Creatine monohydrate, which is frequently consumed alone, does not require meals for absorption.
Third-party testing is essential for complement corporations
to ensure their merchandise are protected, meet regulatory requirements, and construct
shopper confidence. You can take Creatine on an empty abdomen; nevertheless, many people favor to
take it with food. In Accordance to numerous research, Creatine may be very beneficial for
high-intensity exercises and anaerobic workout routines.
It might also assist profit cardio workout routines in a few methods.
Whereas Creatine has primarily been used for growing muscle growth, it
has far more to supply. Most ladies notice improved performance inside 2-4 weeks of
consistent use.
If your causes for fasting dig deeper than simply bodily performance,
there are some things to consider. For many athletes and gym-goers, these advantages easily outweigh the tiny, technical "break" in a strict quick.
They could be minor, but they're still essential if you're aiming
for a "pure" fasting experience.
Now, with that in thoughts, if you’re taking pure creatine, then the reply is not any, it
won’t break your fast, as it has no energy and doesn’t have an effect on your blood insulin ranges.
Technically, creatine could be categorized as a non-protein nitrogen. Therefore, creatine supplementation could be an efficient strategy to
take care of and build muscle mass when mixed
with intermittent fasting’s fat burning effects.
Creatine supplements are in style because analysis has constantly
proven that creatine supplementation can considerably elevate the degrees of creatine in your
muscular tissues. This, in turn, improves your muscles’
capability to generate power throughout high-intensity anaerobic train, resulting in increases in lean muscle mass
and strength. In conclusion, taking creatine supplements
throughout fasting shouldn't break your fast when it comes to calorie consumption.
Creatine performs a crucial role right here by replenishing ATP shops extra
efficiently, which is significant for regeneration and constructing muscle tissues.
However, there are a few water-soluble nutritional vitamins that you can consume without breaking your fast.
You must note that having the best balance of vitamins and minerals is
essential to aiding nutrient replenishment throughout fasting.
Many folks have hunger cravings, nausea, and fatigue when they quick or take sure multivitamins.
Hence, it is essential to consult a health care provider if you're experiencing any health
issues when looking for dietary supplements while fasting.
So as merely put as I can, protein powders are undoubtedly a no-go in relation to fasting.
Dietary sources of creatine include meat, poultry, fish, and
dairy products, though supplementation often offers higher concentrations than meals alone.
The power metabolism process relies heavily on ATP adenosine triphosphate, usually known as the body’s power forex.
Throughout anaerobic activity like weightlifting or sprinting,
muscles quickly deplete their ATP shops. Maintain reading to find out how creatine impacts your fasting objectives.
Nonetheless, be conscious of added components that will contain calories or macronutrients able to disrupting
the fasting state.
Now you have to combine your creatine with water or a low-calorie beverage.
The best thing about creatine monohydrate is that it dissolves easily and is available in powdered type.
Here is a step-by-step guide on tips on how to take creatine
while fasting. Before we handle whether or not you can take
creatine while fasting, it's essential to understand what creatine is
and how fasting works. Creatine isn't only identified for muscle
development, it has other advantages as well. Once you full the loading part,
you probably can then change to a upkeep
dose of 3 to 5g per day to take care of your creatine levels.
Their use ought to solely depend upon the individual and their well being goals.
For greatest outcomes when fasting intermittently, you may profit from taking your supplement only once a day
earlier than a workout. That method, you can get pleasure from the benefits of the additional protein without
taking in too many calories and raising your blood sugar ranges.
thickening agents, preservatives, and additives to make
the most out of your intermittent fasting routine. Individual reactions to creatine
and fasting packages can differ greatly. Metabolism,
stage of activity, and dietary preferences are a number
of examples of the components that have an result on outcomes.
As a result, it's critical to experiment, observe success, and adjust creatine dosage and
fasting techniques as wanted. Personalization is crucial for getting
the most effective results, depending on one's personal wants and goals.
It is pointless to take creatine with food while fasting; it can be absorbed properly on an empty abdomen. Creatine monohydrate, which is frequently consumed alone, does not require meals for absorption.
Third-party testing is essential for complement corporations
to ensure their merchandise are protected, meet regulatory requirements, and construct
shopper confidence. You can take Creatine on an empty abdomen; nevertheless, many people favor to
take it with food. In Accordance to numerous research, Creatine may be very beneficial for
high-intensity exercises and anaerobic workout routines.
It might also assist profit cardio workout routines in a few methods.
Whereas Creatine has primarily been used for growing muscle growth, it
has far more to supply. Most ladies notice improved performance inside 2-4 weeks of
consistent use.
If your causes for fasting dig deeper than simply bodily performance,
there are some things to consider. For many athletes and gym-goers, these advantages easily outweigh the tiny, technical "break" in a strict quick.
They could be minor, but they're still essential if you're aiming
for a "pure" fasting experience.
Now, with that in thoughts, if you’re taking pure creatine, then the reply is not any, it
won’t break your fast, as it has no energy and doesn’t have an effect on your blood insulin ranges.
Technically, creatine could be categorized as a non-protein nitrogen. Therefore, creatine supplementation could be an efficient strategy to
take care of and build muscle mass when mixed
with intermittent fasting’s fat burning effects.
Creatine supplements are in style because analysis has constantly
proven that creatine supplementation can considerably elevate the degrees of creatine in your
muscular tissues. This, in turn, improves your muscles’
capability to generate power throughout high-intensity anaerobic train, resulting in increases in lean muscle mass
and strength. In conclusion, taking creatine supplements
throughout fasting shouldn't break your fast when it comes to calorie consumption.
Creatine performs a crucial role right here by replenishing ATP shops extra
efficiently, which is significant for regeneration and constructing muscle tissues.
However, there are a few water-soluble nutritional vitamins that you can consume without breaking your fast.
You must note that having the best balance of vitamins and minerals is
essential to aiding nutrient replenishment throughout fasting.
Many folks have hunger cravings, nausea, and fatigue when they quick or take sure multivitamins.
Hence, it is essential to consult a health care provider if you're experiencing any health
issues when looking for dietary supplements while fasting.
So as merely put as I can, protein powders are undoubtedly a no-go in relation to fasting.
Dietary sources of creatine include meat, poultry, fish, and
dairy products, though supplementation often offers higher concentrations than meals alone.
The power metabolism process relies heavily on ATP adenosine triphosphate, usually known as the body’s power forex.
Throughout anaerobic activity like weightlifting or sprinting,
muscles quickly deplete their ATP shops. Maintain reading to find out how creatine impacts your fasting objectives.
Nonetheless, be conscious of added components that will contain calories or macronutrients able to disrupting
the fasting state.
Now you have to combine your creatine with water or a low-calorie beverage.
The best thing about creatine monohydrate is that it dissolves easily and is available in powdered type.
Here is a step-by-step guide on tips on how to take creatine
while fasting. Before we handle whether or not you can take
creatine while fasting, it's essential to understand what creatine is
and how fasting works. Creatine isn't only identified for muscle
development, it has other advantages as well. Once you full the loading part,
you probably can then change to a upkeep
dose of 3 to 5g per day to take care of your creatine levels.
Their use ought to solely depend upon the individual and their well being goals.
For greatest outcomes when fasting intermittently, you may profit from taking your supplement only once a day
earlier than a workout. That method, you can get pleasure from the benefits of the additional protein without
taking in too many calories and raising your blood sugar ranges.
[2025-08-20 02:26:11.759803]
URL
(齊藤)
気に入って頂けて良かったです。
こちらこそ是非!白楽でイワシパーティー誘って下さい。
[2013-07-06 23:53:08]
(Y澤タイソン)
すこぶる調子いいですよぉ!!
HALUさんもK-生活に大満足(*^^*)
また飲んでやって下され♪
[2013-07-03 13:12:32]