新車デリカD5 シャモニー納車させていただきました。
2017年12月26日
ご注文いただきました
新車のデリカD5 この季節の特別仕様車シャモニー
クリーンディーゼルを納車させていただきました。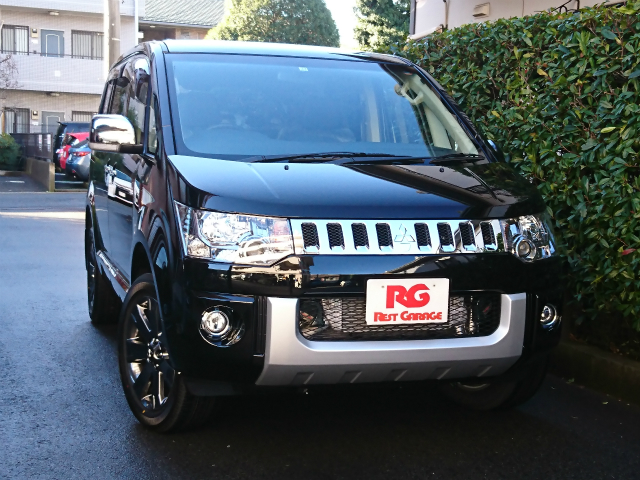


なんと納車日はクリスマス


合わせた訳では無いんですけどね。
24日にボディーにポリマーコーティングを施工したのが最後の作業で
お渡しが25日となりました
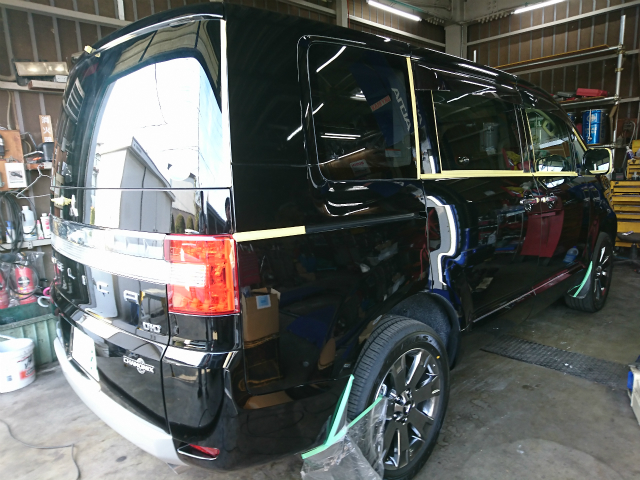

ポリマーコーティング施工中
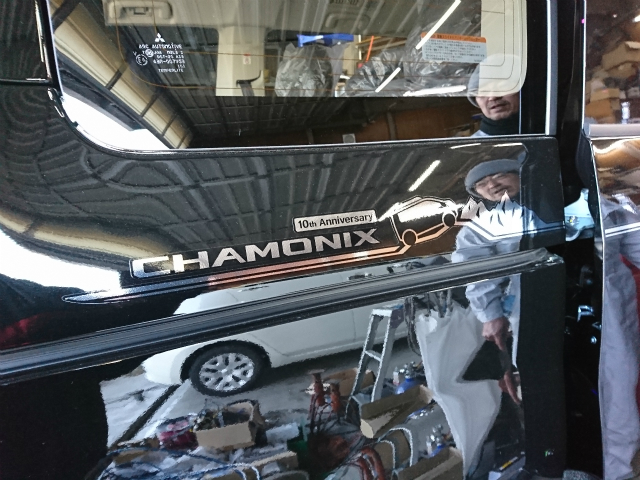

あ、両サイドに貼ってある
10周年記念シャモニーステッカーはご要望で剥がしました。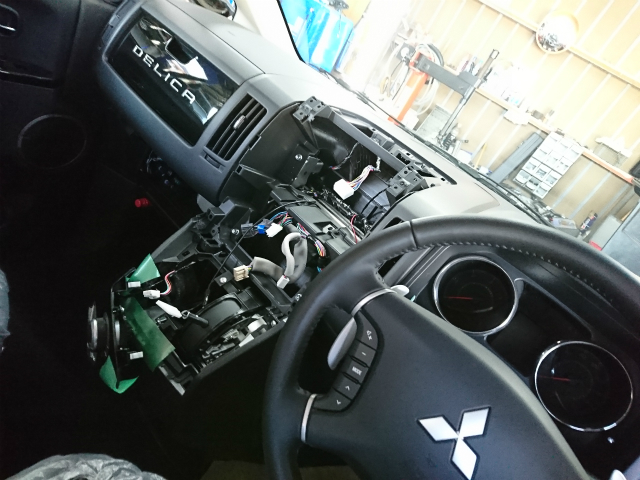
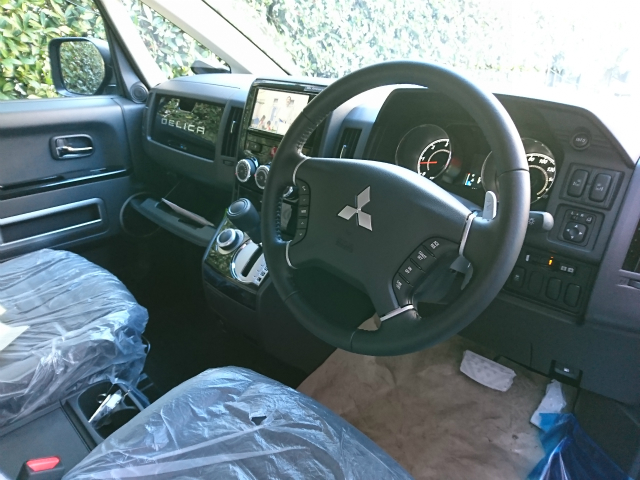
ナビとバックカメラの取り付け作業の様子
バラバラです
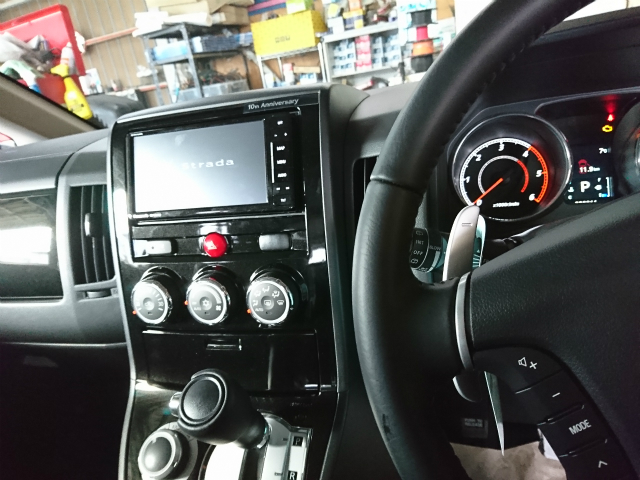


ステアリングリモコン対応ナビなので、操作ラクラクです

デリカはワイドナビが入るので
パナソニックの新しい7型ワイドRE04WDをインストール
取付キットを探すのが大変でした・・・(´・ω・`)
灯台下暗しとはこの事。
純正取り付け金具でOKだとは・・・ (笑)
(笑)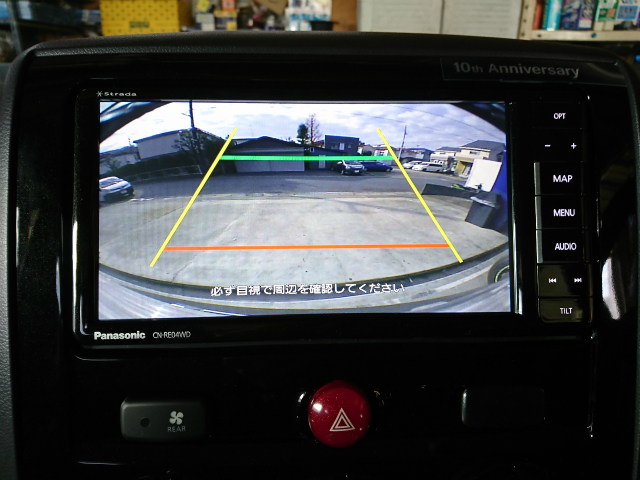
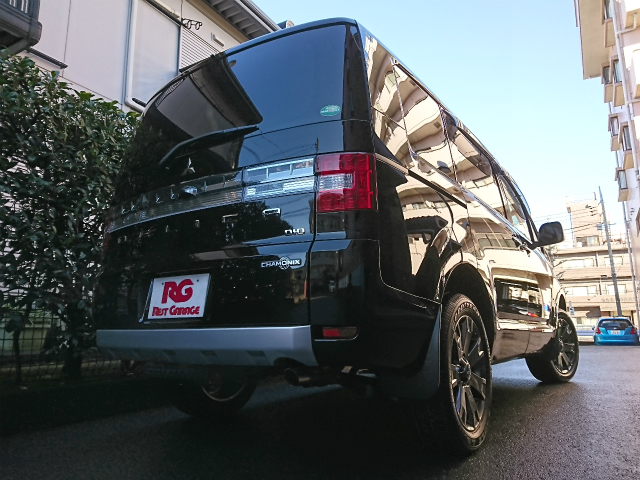
バックカメラもリアガーニッシュ内に綺麗に収まりいい感じです♪
ピッピッッ の純正ホーンだとアレなので、
の純正ホーンだとアレなので、
アルファホーンに変更
来年にはモデルチェンジなデリカD5ですが、
お客さまのご要望どおりの
ステキな最終モデル シャモニーに仕上がりました
ご購入からカスタマイズのお手伝いまで出来て僕も楽しかったです
いつもありがとうございます。
レストガレージ阿部
この記事へのコメント
(Marta)
BPC?157 is a synthetic peptide that has gained attention for its
potential healing properties, especially in sports medicine and recovery from injuries.
While it can be administered through injections, many users are curious about oral formulations such as tablets or capsules, which promise greater convenience.
Understanding the differences between these delivery methods, their benefits, risks,
and how they compare is essential before deciding whether
to incorporate BPC?157 into a treatment regimen.
What is BPC?157 (Body Protection Compound)?
BPC?157, short for Body Protective Compound 157, refers to a fragment of
a protein that naturally occurs in the stomach. The sequence consists of 15 amino acids and is derived from a larger protein called body protection compound.
This peptide has been studied primarily in animal models, where it demonstrated remarkable effects on tissue repair and regeneration. Key
findings include:
Accelerated healing of muscle, tendon, ligament, and bone injuries
Reduction of inflammation through modulation of cytokine levels
Protection against gastric ulcers by enhancing mucosal blood flow
Potential neuroprotective benefits in spinal cord injury models
Because it is a peptide, BPC?157 is inherently unstable when exposed to digestive enzymes.
That has led researchers and manufacturers to develop strategies for
delivering the compound orally in a protected form (such as encapsulation or inclusion in a carrier matrix) that can survive passage through the stomach and reach systemic circulation.
BPC 157 Tablets vs Injection: Benefits, Risks & Comparison
Route of Administration
Injection delivers BPC?157 directly into the bloodstream or near
the target tissue. This method bypasses the gastrointestinal
tract, ensuring rapid absorption and higher bioavailability.
Oral tablets, on the other hand, rely on the compound’s ability to resist enzymatic degradation and be absorbed through the gut lining.
Even with protective formulations, oral delivery typically results in lower systemic levels than injections.
Ease of Use
Tablets are self?administered, portable, and do not require needles or sterile equipment.
They also eliminate the discomfort associated with repeated injections.
In contrast, injection requires a syringe, needles, and proper technique to avoid contamination or injury.
Compliance & Convenience
Because tablets can be taken daily without medical supervision, they
tend to encourage better adherence to a prescribed
regimen. Injections may be limited by clinic visits
or self?injection training, which some users find cumbersome.
Onset of Action
Injectable BPC?157 produces noticeable effects within minutes
to hours, depending on dosage and site of injection. Oral tablets generally have a delayed onset; it can take several days of consistent
use before the cumulative effect becomes evident.
Safety Profile
Both forms share similar safety concerns related to dosage and potential
side effects. However, injections carry an additional risk
of infection or local tissue irritation if not performed correctly.
Oral administration eliminates this specific risk but may introduce gastrointestinal discomfort in sensitive individuals, especially when taken on an empty stomach.
Cost Considerations
Injectable BPC?157 is usually more expensive due
to the need for sterile production and packaging.
Tablets are often priced lower per dose, making them a budget-friendly option for long-term use.
Bioavailability & Efficacy
Studies indicate that injectable BPC?157 achieves
higher plasma concentrations, which correlates with stronger
therapeutic outcomes in acute injury settings. Oral tablets,
while easier to administer, may require higher doses or longer treatment periods to match the efficacy seen with injections.
Potential for Misuse
Because injections can produce a rapid response, there is a risk that users might over?dose or
use them for non?medical purposes (e.g., performance enhancement).
Tablets’ slower action reduces this temptation but does not eliminate
it entirely.
Key Takeaways
BPC?157 is a peptide derived from a stomach protein that shows promise in accelerating tissue
repair and reducing inflammation.
Oral tablets offer convenience, lower risk of infection, and better compliance but usually deliver the compound
at lower systemic levels compared to injections.
Injections provide rapid absorption, higher
bioavailability, and stronger acute effects, yet require sterile technique and carry injection?related risks.
The choice between tablet and injection depends on the user’s goals: quick healing for
an acute injury may favor injections; ongoing maintenance or recovery might be
better served by tablets.
Regardless of delivery method, proper dosing, sourcing from reputable suppliers,
and monitoring for side effects remain crucial to maximize
benefits while minimizing potential harms.
potential healing properties, especially in sports medicine and recovery from injuries.
While it can be administered through injections, many users are curious about oral formulations such as tablets or capsules, which promise greater convenience.
Understanding the differences between these delivery methods, their benefits, risks,
and how they compare is essential before deciding whether
to incorporate BPC?157 into a treatment regimen.
What is BPC?157 (Body Protection Compound)?
BPC?157, short for Body Protective Compound 157, refers to a fragment of
a protein that naturally occurs in the stomach. The sequence consists of 15 amino acids and is derived from a larger protein called body protection compound.
This peptide has been studied primarily in animal models, where it demonstrated remarkable effects on tissue repair and regeneration. Key
findings include:
Accelerated healing of muscle, tendon, ligament, and bone injuries
Reduction of inflammation through modulation of cytokine levels
Protection against gastric ulcers by enhancing mucosal blood flow
Potential neuroprotective benefits in spinal cord injury models
Because it is a peptide, BPC?157 is inherently unstable when exposed to digestive enzymes.
That has led researchers and manufacturers to develop strategies for
delivering the compound orally in a protected form (such as encapsulation or inclusion in a carrier matrix) that can survive passage through the stomach and reach systemic circulation.
BPC 157 Tablets vs Injection: Benefits, Risks & Comparison
Route of Administration
Injection delivers BPC?157 directly into the bloodstream or near
the target tissue. This method bypasses the gastrointestinal
tract, ensuring rapid absorption and higher bioavailability.
Oral tablets, on the other hand, rely on the compound’s ability to resist enzymatic degradation and be absorbed through the gut lining.
Even with protective formulations, oral delivery typically results in lower systemic levels than injections.
Ease of Use
Tablets are self?administered, portable, and do not require needles or sterile equipment.
They also eliminate the discomfort associated with repeated injections.
In contrast, injection requires a syringe, needles, and proper technique to avoid contamination or injury.
Compliance & Convenience
Because tablets can be taken daily without medical supervision, they
tend to encourage better adherence to a prescribed
regimen. Injections may be limited by clinic visits
or self?injection training, which some users find cumbersome.
Onset of Action
Injectable BPC?157 produces noticeable effects within minutes
to hours, depending on dosage and site of injection. Oral tablets generally have a delayed onset; it can take several days of consistent
use before the cumulative effect becomes evident.
Safety Profile
Both forms share similar safety concerns related to dosage and potential
side effects. However, injections carry an additional risk
of infection or local tissue irritation if not performed correctly.
Oral administration eliminates this specific risk but may introduce gastrointestinal discomfort in sensitive individuals, especially when taken on an empty stomach.
Cost Considerations
Injectable BPC?157 is usually more expensive due
to the need for sterile production and packaging.
Tablets are often priced lower per dose, making them a budget-friendly option for long-term use.
Bioavailability & Efficacy
Studies indicate that injectable BPC?157 achieves
higher plasma concentrations, which correlates with stronger
therapeutic outcomes in acute injury settings. Oral tablets,
while easier to administer, may require higher doses or longer treatment periods to match the efficacy seen with injections.
Potential for Misuse
Because injections can produce a rapid response, there is a risk that users might over?dose or
use them for non?medical purposes (e.g., performance enhancement).
Tablets’ slower action reduces this temptation but does not eliminate
it entirely.
Key Takeaways
BPC?157 is a peptide derived from a stomach protein that shows promise in accelerating tissue
repair and reducing inflammation.
Oral tablets offer convenience, lower risk of infection, and better compliance but usually deliver the compound
at lower systemic levels compared to injections.
Injections provide rapid absorption, higher
bioavailability, and stronger acute effects, yet require sterile technique and carry injection?related risks.
The choice between tablet and injection depends on the user’s goals: quick healing for
an acute injury may favor injections; ongoing maintenance or recovery might be
better served by tablets.
Regardless of delivery method, proper dosing, sourcing from reputable suppliers,
and monitoring for side effects remain crucial to maximize
benefits while minimizing potential harms.
[2025-10-06 20:25:01.856115]
URL
(Mike)
Anavar, chemically known as oxandrolone, is a synthetic
anabolic steroid widely used for its mild androgenic properties and its ability to promote lean muscle mass while minimizing fat gain. Understanding
how to calculate an effective dosage involves not only knowing the
drug’s pharmacokinetics?particularly its
half?life?but also considering factors such as individual metabolism,
desired outcomes, and cycle length.
Anavar Half Life Timing: Dosage and Calculation
The average elimination half?life of oxandrolone in a healthy adult ranges from 9 to 10 hours.
Because the drug’s plasma concentration declines by roughly half every nine
hours, it is common practice to schedule doses at intervals that keep serum levels within an optimal therapeutic window.
For most users aiming for moderate anabolic effects while minimizing side?effects,
a twice?daily dosing regimen works well. To calculate the daily dose, first
decide on the total milligrams you wish to ingest
per day; common ranges are 10 mg, 20 mg, or 30 mg depending on experience level and
goals. If you choose a 20?mg daily target and plan two doses, each
injection will be 10 mg. This division keeps plasma concentrations relatively steady: after the
first dose peaks around the hour mark, the second dose administered approximately twelve hours later overlaps with the tail end of the first dose’s
effect, maintaining a near?constant level without abrupt spikes.
When considering longer cycles or higher doses?say 40 mg per day?split
into two 20?mg administrations. Here the overlap is more pronounced; the drug will still be present in significant amounts for up to eighteen hours after the initial injection, and only gradually falls below therapeutic thresholds toward
the cycle’s end. This pattern reduces the risk of sudden withdrawal symptoms that might otherwise occur if a single large dose were taken.
What is Anavar's Half?Life?
A half?life is the time required for the concentration of a drug in the bloodstream to reduce by 50 percent.
For oxandrolone, the reported average lies between nine and ten hours, but individual differences can extend this period up
to twelve or thirteen hours in some cases. Factors influencing this variability include age,
liver function, concurrent medications, and genetic predispositions affecting metabolic enzymes like CYP3A4.
The relatively short half?life compared with other anabolic steroids means that Anavar does not accumulate heavily
over a cycle; instead, it provides steady anabolic support while allowing the body to clear excess amounts quickly.
Because of this pharmacokinetic profile, users often schedule doses
in the morning and late afternoon or evening.
A typical schedule might look like 08:00 for the first dose and 20:00 for the second.
With a nine?hour half?life, the drug concentration after the first dose
peaks around 10?12 hours later, while the second dose
maintains levels above baseline until about twenty?five
to thirty hours post?first injection. This overlapping window is crucial for achieving sustained anabolic activity without the
high peaks that can trigger androgenic side effects.
Related Considerations
Cycle Length and End-of-Cycle Tapering: Because of its relatively short half?life, Anavar’s elimination after cycle
completion occurs rapidly. Users often incorporate a tapering
phase?reducing daily dosage by 5 mg every few days?to prevent sudden withdrawal symptoms such as
fatigue or mood swings.
Post Cycle Therapy (PCT): Even though oxandrolone has minimal impact on the hypothalamic?pituitary?gonadal axis, users who have combined it with other steroids may need a short PCT regimen to support natural testosterone production once the cycle ends.
Typical agents include clomiphene citrate or tamoxifen, dosed according to individual hormone levels.
Monitoring Liver Function: Despite being one of the milder liver?stressors among
oral anabolic steroids, Anavar still requires periodic assessment of liver enzymes (ALT, AST).
A sudden rise in these markers may signal hepatic strain, warranting dose adjustment or cycle termination.
Personalized Dose Adjustments: Beginners often start at 10 mg per day
to gauge tolerance. Experienced users who have built a baseline resistance to androgenic side effects might push
up to 30?40 mg daily if they seek maximal lean mass
gains while still staying within safe limits.
Timing with Meals and Supplements: Oxandrolone is lipophilic, meaning it dissolves
better in fats. Consuming the drug with a meal that contains healthy
oils can improve absorption rates, thereby enhancing its effectiveness without increasing
dose.
Hydration and Protein Intake: Adequate water consumption helps maintain kidney filtration of metabolites, while high?quality protein supports anabolic processes stimulated by Anavar.
Pairing the steroid with leucine?rich foods or supplements
ensures amino acids are available for muscle repair and growth.
In summary, calculating an Anavar dosage hinges on understanding its nine?to?ten hour half?life, which dictates a twice?daily schedule for most users.
By dividing total daily mg into two equal portions,
aligning doses to the drug’s pharmacokinetic profile, and monitoring physiological responses?including liver enzymes
and hormone levels?users can optimize anabolic benefits while keeping side effects in check.
Adjustments for cycle length, tapering protocols, and individualized tolerance further refine dosing strategy,
allowing athletes and bodybuilders to harness
Anavar’s lean?mass advantages responsibly.
anabolic steroid widely used for its mild androgenic properties and its ability to promote lean muscle mass while minimizing fat gain. Understanding
how to calculate an effective dosage involves not only knowing the
drug’s pharmacokinetics?particularly its
half?life?but also considering factors such as individual metabolism,
desired outcomes, and cycle length.
Anavar Half Life Timing: Dosage and Calculation
The average elimination half?life of oxandrolone in a healthy adult ranges from 9 to 10 hours.
Because the drug’s plasma concentration declines by roughly half every nine
hours, it is common practice to schedule doses at intervals that keep serum levels within an optimal therapeutic window.
For most users aiming for moderate anabolic effects while minimizing side?effects,
a twice?daily dosing regimen works well. To calculate the daily dose, first
decide on the total milligrams you wish to ingest
per day; common ranges are 10 mg, 20 mg, or 30 mg depending on experience level and
goals. If you choose a 20?mg daily target and plan two doses, each
injection will be 10 mg. This division keeps plasma concentrations relatively steady: after the
first dose peaks around the hour mark, the second dose administered approximately twelve hours later overlaps with the tail end of the first dose’s
effect, maintaining a near?constant level without abrupt spikes.
When considering longer cycles or higher doses?say 40 mg per day?split
into two 20?mg administrations. Here the overlap is more pronounced; the drug will still be present in significant amounts for up to eighteen hours after the initial injection, and only gradually falls below therapeutic thresholds toward
the cycle’s end. This pattern reduces the risk of sudden withdrawal symptoms that might otherwise occur if a single large dose were taken.
What is Anavar's Half?Life?
A half?life is the time required for the concentration of a drug in the bloodstream to reduce by 50 percent.
For oxandrolone, the reported average lies between nine and ten hours, but individual differences can extend this period up
to twelve or thirteen hours in some cases. Factors influencing this variability include age,
liver function, concurrent medications, and genetic predispositions affecting metabolic enzymes like CYP3A4.
The relatively short half?life compared with other anabolic steroids means that Anavar does not accumulate heavily
over a cycle; instead, it provides steady anabolic support while allowing the body to clear excess amounts quickly.
Because of this pharmacokinetic profile, users often schedule doses
in the morning and late afternoon or evening.
A typical schedule might look like 08:00 for the first dose and 20:00 for the second.
With a nine?hour half?life, the drug concentration after the first dose
peaks around 10?12 hours later, while the second dose
maintains levels above baseline until about twenty?five
to thirty hours post?first injection. This overlapping window is crucial for achieving sustained anabolic activity without the
high peaks that can trigger androgenic side effects.
Related Considerations
Cycle Length and End-of-Cycle Tapering: Because of its relatively short half?life, Anavar’s elimination after cycle
completion occurs rapidly. Users often incorporate a tapering
phase?reducing daily dosage by 5 mg every few days?to prevent sudden withdrawal symptoms such as
fatigue or mood swings.
Post Cycle Therapy (PCT): Even though oxandrolone has minimal impact on the hypothalamic?pituitary?gonadal axis, users who have combined it with other steroids may need a short PCT regimen to support natural testosterone production once the cycle ends.
Typical agents include clomiphene citrate or tamoxifen, dosed according to individual hormone levels.
Monitoring Liver Function: Despite being one of the milder liver?stressors among
oral anabolic steroids, Anavar still requires periodic assessment of liver enzymes (ALT, AST).
A sudden rise in these markers may signal hepatic strain, warranting dose adjustment or cycle termination.
Personalized Dose Adjustments: Beginners often start at 10 mg per day
to gauge tolerance. Experienced users who have built a baseline resistance to androgenic side effects might push
up to 30?40 mg daily if they seek maximal lean mass
gains while still staying within safe limits.
Timing with Meals and Supplements: Oxandrolone is lipophilic, meaning it dissolves
better in fats. Consuming the drug with a meal that contains healthy
oils can improve absorption rates, thereby enhancing its effectiveness without increasing
dose.
Hydration and Protein Intake: Adequate water consumption helps maintain kidney filtration of metabolites, while high?quality protein supports anabolic processes stimulated by Anavar.
Pairing the steroid with leucine?rich foods or supplements
ensures amino acids are available for muscle repair and growth.
In summary, calculating an Anavar dosage hinges on understanding its nine?to?ten hour half?life, which dictates a twice?daily schedule for most users.
By dividing total daily mg into two equal portions,
aligning doses to the drug’s pharmacokinetic profile, and monitoring physiological responses?including liver enzymes
and hormone levels?users can optimize anabolic benefits while keeping side effects in check.
Adjustments for cycle length, tapering protocols, and individualized tolerance further refine dosing strategy,
allowing athletes and bodybuilders to harness
Anavar’s lean?mass advantages responsibly.
[2025-10-06 17:44:49.7119]
URL
(Madge)
Ipamorelin and CJC?1295 are two of the most popular growth hormone secretagogues used
by athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals seeking anti?aging
benefits. While they can provide significant increases in circulating
growth hormone levels, their use is not without risks. Understanding the potential side effects, especially from a medical perspective, helps users
make informed decisions about whether to incorporate these peptides into their regimen.
---
Understanding Ipamorelin Side Effects: A Comprehensive Review
Hormonal Imbalance and Endocrine Disruption
Ipamorelin stimulates the pituitary gland to release growth
hormone (GH) and insulin?like growth factor 1 (IGF?1).
Prolonged or high?dose exposure can upset
the delicate balance of other hormones. Users may experience:
Elevated prolactin levels, which can lead to lactation in women, decreased libido, and sexual dysfunction.
Alterations in thyroid hormone production; some individuals report mild hypothyroidism symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, or cold intolerance.
Changes in cortisol rhythm, potentially contributing to
mood swings or sleep disturbances.
Metabolic Effects
Because growth hormone has lipolytic properties, it can influence glucose metabolism.
The main metabolic concerns include:
Insulin resistance: Some users develop higher fasting insulin levels and decreased glucose tolerance over time,
which may predispose them to type?2 diabetes.
Increased triglycerides: Elevated fat breakdown can sometimes raise circulating lipid intermediates, potentially
impacting cardiovascular risk.
Local Injection Site Reactions
Ipamorelin is typically administered subcutaneously. Common local
reactions involve:
Redness and swelling at the injection site that generally resolves within 24
to 48 hours.
Pain or tenderness during needle insertion or withdrawal.
Rarely, users develop a mild inflammatory reaction that may
require topical steroids or antihistamines.
Cardiovascular Concerns
Growth hormone exerts effects on blood vessels.
In susceptible individuals, ipamorelin can cause:
Peripheral edema: Fluid retention in extremities, especially when combined with high GH levels.
Hypertension: Elevated blood pressure readings may appear after
prolonged use, necessitating regular monitoring.
Neurological and Psychological Effects
Some users report changes in mood or cognition, which may include:
Anxiety or irritability during the first weeks of therapy as the body adapts to increased GH.
Sleep disturbances such as insomnia or vivid dreams due to hormonal fluctuations.
Headaches, particularly if water retention leads to increased intracranial pressure.
Rare but Serious Complications
Although uncommon, there are serious adverse events that can arise:
Acromegalic changes: Long?term overstimulation of GH can lead to soft tissue
swelling and bone overgrowth in the hands, feet, or
face.
Tumor growth stimulation: Certain tumors
may respond to higher IGF?1 levels by accelerating proliferation.
Key Takeaways
Dose Matters ? The likelihood and severity of side effects
increase with higher dosages or extended treatment
periods. Adhering to recommended protocols (e.g., 100?200??g daily) reduces risk.
Monitoring is Crucial ? Regular blood work for GH, IGF?1,
insulin, thyroid hormones, and lipid panels helps catch imbalances early.
Injection Technique Affects Comfort ? Using a new sterile needle
each time and rotating injection sites can minimize
local reactions.
Lifestyle Factors Influence Outcomes ? Adequate sleep,
balanced nutrition, and avoiding excessive alcohol or
caffeine help mitigate many side effects.
Consult Healthcare Professionals ? Prior to starting ipamorelin, especially if you have pre?existing medical conditions, a thorough
evaluation by an endocrinologist is advisable.
Ipamorelin Cancer Risk Assessment
The relationship between growth hormone secretagogues and cancer risk remains under investigation.
Several points are important:
Biological Rationale
Growth hormone drives the production of IGF?1, a mitogenic factor that can promote cell proliferation. Elevated IGF?1 levels have been linked in epidemiological studies
to increased risks for certain cancers such as breast,
prostate, and colorectal.
Evidence from Animal Studies
Rodent models treated with GH secretagogues occasionally show accelerated tumor growth in pre?existing tumors or enhanced development of benign nodules.
However, translating these findings to humans is not straightforward due to species differences.
Human Data
Clinical trials involving ipamorelin are limited and typically short?term
(a few weeks). No large?scale randomized controlled studies
have definitively shown an increase in cancer incidence among users.
Long?term observational data are sparse.
Current Consensus
Low to Moderate Risk: For healthy individuals using standard therapeutic doses, the risk appears low but cannot
be dismissed entirely.
Higher Risk with Pre?Existing Conditions: People who already have hormone?responsive cancers or a strong family history may face
an elevated risk if GH/IGF?1 levels rise.
Practical Recommendations
Screening Before Use ? A baseline evaluation of tumor markers and imaging for those with personal or familial cancer histories can identify hidden lesions.
Periodic Surveillance ? Annual check?ups, including PSA testing in men over 50,
mammography in women, and colonoscopy as indicated, are prudent while
on therapy.
Limit Duration ? Shorter courses (no more than three to six months)
reduce cumulative exposure to elevated IGF?1.
In summary, while ipamorelin offers tangible benefits for growth hormone deficiency or anti?aging protocols, it carries a spectrum of
side effects ranging from mild injection site reactions to serious endocrine and cardiovascular disturbances.
Its potential link to cancer remains an area of active research;
thus, users should proceed with caution, maintain rigorous monitoring, and
consult healthcare providers before initiating therapy.
by athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals seeking anti?aging
benefits. While they can provide significant increases in circulating
growth hormone levels, their use is not without risks. Understanding the potential side effects, especially from a medical perspective, helps users
make informed decisions about whether to incorporate these peptides into their regimen.
---
Understanding Ipamorelin Side Effects: A Comprehensive Review
Hormonal Imbalance and Endocrine Disruption
Ipamorelin stimulates the pituitary gland to release growth
hormone (GH) and insulin?like growth factor 1 (IGF?1).
Prolonged or high?dose exposure can upset
the delicate balance of other hormones. Users may experience:
Elevated prolactin levels, which can lead to lactation in women, decreased libido, and sexual dysfunction.
Alterations in thyroid hormone production; some individuals report mild hypothyroidism symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, or cold intolerance.
Changes in cortisol rhythm, potentially contributing to
mood swings or sleep disturbances.
Metabolic Effects
Because growth hormone has lipolytic properties, it can influence glucose metabolism.
The main metabolic concerns include:
Insulin resistance: Some users develop higher fasting insulin levels and decreased glucose tolerance over time,
which may predispose them to type?2 diabetes.
Increased triglycerides: Elevated fat breakdown can sometimes raise circulating lipid intermediates, potentially
impacting cardiovascular risk.
Local Injection Site Reactions
Ipamorelin is typically administered subcutaneously. Common local
reactions involve:
Redness and swelling at the injection site that generally resolves within 24
to 48 hours.
Pain or tenderness during needle insertion or withdrawal.
Rarely, users develop a mild inflammatory reaction that may
require topical steroids or antihistamines.
Cardiovascular Concerns
Growth hormone exerts effects on blood vessels.
In susceptible individuals, ipamorelin can cause:
Peripheral edema: Fluid retention in extremities, especially when combined with high GH levels.
Hypertension: Elevated blood pressure readings may appear after
prolonged use, necessitating regular monitoring.
Neurological and Psychological Effects
Some users report changes in mood or cognition, which may include:
Anxiety or irritability during the first weeks of therapy as the body adapts to increased GH.
Sleep disturbances such as insomnia or vivid dreams due to hormonal fluctuations.
Headaches, particularly if water retention leads to increased intracranial pressure.
Rare but Serious Complications
Although uncommon, there are serious adverse events that can arise:
Acromegalic changes: Long?term overstimulation of GH can lead to soft tissue
swelling and bone overgrowth in the hands, feet, or
face.
Tumor growth stimulation: Certain tumors
may respond to higher IGF?1 levels by accelerating proliferation.
Key Takeaways
Dose Matters ? The likelihood and severity of side effects
increase with higher dosages or extended treatment
periods. Adhering to recommended protocols (e.g., 100?200??g daily) reduces risk.
Monitoring is Crucial ? Regular blood work for GH, IGF?1,
insulin, thyroid hormones, and lipid panels helps catch imbalances early.
Injection Technique Affects Comfort ? Using a new sterile needle
each time and rotating injection sites can minimize
local reactions.
Lifestyle Factors Influence Outcomes ? Adequate sleep,
balanced nutrition, and avoiding excessive alcohol or
caffeine help mitigate many side effects.
Consult Healthcare Professionals ? Prior to starting ipamorelin, especially if you have pre?existing medical conditions, a thorough
evaluation by an endocrinologist is advisable.
Ipamorelin Cancer Risk Assessment
The relationship between growth hormone secretagogues and cancer risk remains under investigation.
Several points are important:
Biological Rationale
Growth hormone drives the production of IGF?1, a mitogenic factor that can promote cell proliferation. Elevated IGF?1 levels have been linked in epidemiological studies
to increased risks for certain cancers such as breast,
prostate, and colorectal.
Evidence from Animal Studies
Rodent models treated with GH secretagogues occasionally show accelerated tumor growth in pre?existing tumors or enhanced development of benign nodules.
However, translating these findings to humans is not straightforward due to species differences.
Human Data
Clinical trials involving ipamorelin are limited and typically short?term
(a few weeks). No large?scale randomized controlled studies
have definitively shown an increase in cancer incidence among users.
Long?term observational data are sparse.
Current Consensus
Low to Moderate Risk: For healthy individuals using standard therapeutic doses, the risk appears low but cannot
be dismissed entirely.
Higher Risk with Pre?Existing Conditions: People who already have hormone?responsive cancers or a strong family history may face
an elevated risk if GH/IGF?1 levels rise.
Practical Recommendations
Screening Before Use ? A baseline evaluation of tumor markers and imaging for those with personal or familial cancer histories can identify hidden lesions.
Periodic Surveillance ? Annual check?ups, including PSA testing in men over 50,
mammography in women, and colonoscopy as indicated, are prudent while
on therapy.
Limit Duration ? Shorter courses (no more than three to six months)
reduce cumulative exposure to elevated IGF?1.
In summary, while ipamorelin offers tangible benefits for growth hormone deficiency or anti?aging protocols, it carries a spectrum of
side effects ranging from mild injection site reactions to serious endocrine and cardiovascular disturbances.
Its potential link to cancer remains an area of active research;
thus, users should proceed with caution, maintain rigorous monitoring, and
consult healthcare providers before initiating therapy.
[2025-10-05 21:10:28.440184]
URL